Ecosystem
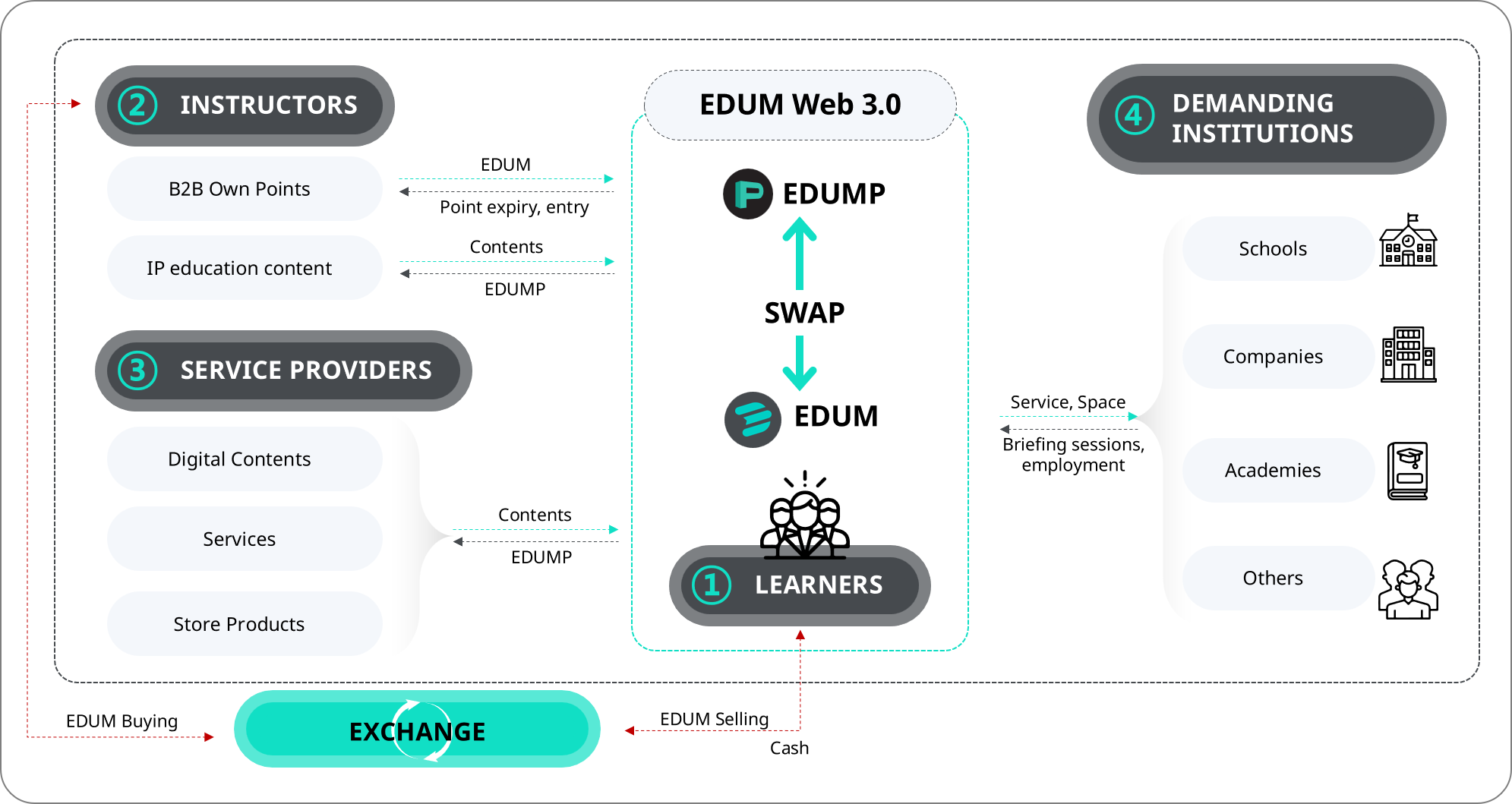
The EDUM ecosystem consists of "Learners," "Educators," "Service Providers," and "Demand Institutions," forming symbiotic and strategic partnerships based on various activities and mutual cooperation. Through the EDUM ecosystem, each participant can efficiently utilize their resources and expertise, pursuing strategic business operations and service diversity.
Additionally, to minimize potential issues such as conflicting interests, information asymmetry, and public responsibility evasion that may arise from the participation of diverse stakeholders, implementing various support and improvement mechanisms within the EDUM ecosystem are planned. The EDUM ecosystem, designed with system convenience (standard protocols and public interfaces), service stability (server technology expertise, SWAP, etc.), and a rational compensation system, can be implemented efficiently and swiftly.
Ecosystem Participants
Learners Learners are users who engage in activities such as participation, purchasing, trading, and communication within the EDUM ecosystem. They serve as the foundation of EDUM ecosystem activities and play the role of both consumers and producers, known as "prosumers." Learners are rewarded based on their engagement and contributions to the ecosystem's activities, such as through the use of Apps/Devices/B2B services. They can use their earned rewards to purchase high-quality content within the EDUM platform or exchange them for tokens and convert them into cash. Through partnerships with domestic and international online learning companies, we plan to expand various types of teacher ecosystems.
Educators Educators play a vital role in the EDUM ecosystem by providing educational content and services related to learning, growth, online lectures, problem-solving, college admissions consulting, career consulting, mentoring, and more. In the early stages of the business, the focus is on corporate content. However, after the establishment of the WEB 3.0 & NFT system, the expansion includes personal Intellectual Property (IP) such as Problem IPs, concentration brainwave data, study techniques, and more. EDUM is also collaborating with KAIST to develop learning measurement AI algorithms, with plans to engage in joint ventures with online learning companies both domestically and internationally. By leveraging these services, Edum aims to expand its ecosystem of educators in various forms.
Service Providers Service providers in the EDUM ecosystem offer a wide range of online and offline products and services related to EDUM's own products (EDU Device, NFT, etc.) and educational content. Online learning companies interested in joining the EDUM ecosystem are expected to play a role in token usage and contribute to the demand for tokens. The EDUM ecosystem offers attractive business opportunities to service providers with its clear targeting of Users (Learners) and advantages such as a rational reward and revenue structure.
Moreover, leveraging the EDUMP token's SWAP system enables various services such as content exchange and sales, attracting new users, publishing, and channeling services. This opens up new business opportunities for different educational companies within the ecosystem.
Demand Institutions Demand institutions within the EDUM ecosystem consist of businesses and organizations that organize seminars, exhibitions, and other events targeting learners and educators, as well as schools, academies, and government agencies that utilize the EDUM platform. Participants from demand institutions primarily make use of tangible services or products rather than intangible content. This also includes social systems that enable the utilization of acquired educational content over time.
The Circular Structure of the Ecosystem
In contrast to the one-way flow of funds typically observed in traditional systems, the EDUM ecosystem is designed with a circular structure that allows for two-way financial flows, where users can transition between being consumers and producers, complementing and expanding each other's roles. This interconnected system promotes cooperation among ecosystem participants, strengthening their social interdependence rather than operating within independent and distinct domains.
By reinforcing roles, rewards, and goals, this framework fosters mutual dependencies and facilitative interactions among the participants. The EDUM ecosystem is implemented with diverse and tangible business models that support a sustainable and cyclical model. It not only provides a blueprint for a sustainable circular model but also establishes itself as an advanced utility token with extensive functionality.

Last updated